Metallurgical Abstracts on Light Metals and Alloys vol.57
Microstructure and Strength of Ti-6Al-4V Samples Additively Manufactured with TiC Heterogeneous Nucleation Site Particles
Yoshimi Watanabe1, Shintaro Yamada1, Tadachika Chiba1, Hisashi Sato1, Seiji Miura2, Kenshiro Abe3 and Tomotsugu Kato3
1 Nagoya Institute of Technology, Nagoya 466-8555, Japan
2 Hokkaido University, Sapporo 060-8628, Japan
3 Nabtesco Corporation, Tokyo 102-0093, Japan
[Published in Materials, 16, No. 17, 5974 (17 pages) (2023)]
https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16175974
E-mail: yoshimi[at]nitech.ac.jp
Key Words: Additive manufacturing, Powder bed fusion (PBF), Ti-6Al-4V alloy, Heterogeneous nucleation site particles, Lattice matching, Tensile test, Single track test
Our research aims to investigate the fabrication of additively manufactured (AMed) Ti-6Al-4V samples under reduced power with the addition of TiC heterogeneous nucleation site particles. For this aim, Ti-6Al-4V samples are fabricated with and without TiC heterogeneous nucleation site particles using an EOS M 290 machine under optimal parameters and reduced power conditions. The microstructure and tensile behavior of the produced samples were studied. In addition, a single-track test was performed to obtain a good understanding of the suppression of gas pores and balling formation with the addition of TiC heterogeneous nucleation site particles. It was found that the formation of gas pores and balling was suppressed with the addition of heterogeneous nucleation site particles within the metallic powder.
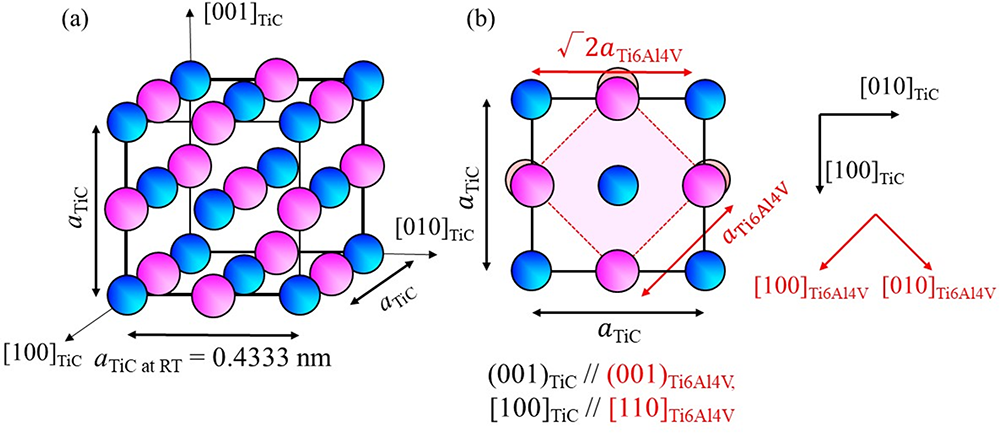
(a) Crystal structure of TiC and (b) atomic arrangement of the (001)TiC plane superimposed on the atomic arrangement of (001)Ti6Al4V.
