Metallurgical Abstracts on Light Metals and Alloys vol.57
Edge Joining of A6061 Aluminum Alloy Sheets by Electrodeposition of Copper
Masataka Hakamada*, Soya Hirose*, Yuki Yamamoto*, Xinsheng Huang**, Isao Nakatsugawa**, Yasumasa Chino**, Hiromi Nakano*** and Mamoru Mabuchi*
* Graduate School of Energy Science, Kyoto University
** Multi-Material Research Institute, National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology
*** Cooperative Research Facility Center, Toyohashi University of Technology
[Published in Materials Transactions, Vol. 64 (2023), pp. 2328-2332]
https://doi.org/10.2320/matertrans.MT-M2023034
E-mail: mabuchi[at]energy.kyoto-u.ac.jp
Key Words: A6061 aluminum alloy, Anodic aluminum oxide, Copper, Electrodeposition joining, Interface
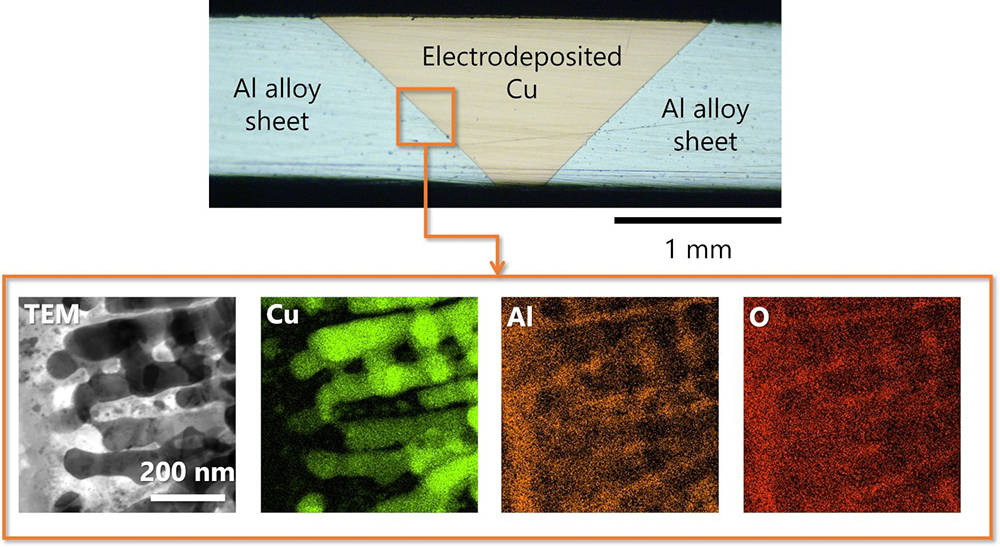
T6-tempered A6061 aluminum alloy sheets were edge joined using electrodeposited copper. Anodic oxidation of the aluminum alloy substrates improved the resulting join strength. This observation is attributed to the nanoanchor effect—mechanical interlocking between the nanoporous structure of anodic aluminum oxides (AAOs) and the electrodeposited copper. A tensile join strength of 214 MPa was obtained when the sheets were joined in an electroplating bath containing thiourea. The microstructures at the AAOs/copper interface were observed using scanning and transmission electron microscopies to elucidate the underlying mechanism of the high join strength. Mechanical strengthening of the electrodeposited copper is necessary for further strengthening of the joint.