Metallurgical Abstracts on Light Metals and Alloys vol.57
Simultaneous intermetallics suppression and residual-stress relaxation of heat-resistant Nb-interlayer-inserted Ti-6Al-4V/Si3N4 joints via one-step transient liquid phase bonding and brazing
Fei Shen Ong*, **, Hirobumi Tobe* and Eiichi Sato*
* Institute of Space and Astronautical Science, Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (ISAS/JAXA)
** Department of Materials Engineering, the University of Tokyo
[Published in Journal of Materials Science & Technology 139 (2023) 79-91]
E-mail: sato[at]isas.jaxa.jp
Key Words: brazing, transient-liquid-phase bonding, CTE mismatch, intermetallics
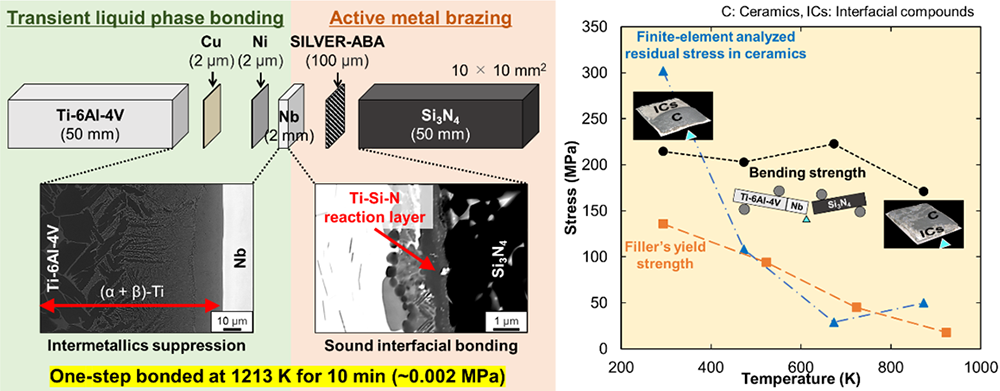
This work has successfully proposed a solution to produce robust Nb-interlayer-inserted Ti-6Al-4V/Si3N4 joints optimized for a maximum operating temperature of 873 K; transient liquid phase bonding (TLPB) of Ti-6Al-4V/Nb side was carried out with Cu and Ni fillers to suppress brittle intermetallic compounds (IMCs), whereas brazing of Nb/Si3N4 side was performed using a highly ductile Ti-added Ag-rich filler for effective residual-stress relaxation. A sound yet simple one-step bonding process incorporating simultaneous TLPB and brazing was achieved with a relatively short holding time of 10 min at 1213 K. TLPB of Ti-6Al-4V/Nb side with Cu and Ni foils of 2-µm-thick each as a laminated filler suppressed brittle Ti-based IMCs and developed a homogenized microstructure consisting mainly of (α+β)-Ti via isothermal solidification. Meanwhile, brazing of Nb/Si3N4 side with 100-µm-thick SILVER-ABA filler (92.75Ag-5Cu-1Al-1.25Ti mass%) foil enhanced interfacial bonding with sufficient total Ti content and accommodated residual stress better than conventional eutectic Ag-Cu-based fillers, and it was verified by finite element analysis with consideration of materials’ temperature-dependent elasto-plastic properties. All joints with a bonding area of 10 mm×10 mm were tested via symmetrical four-point bending from room temperature (RT) to 873 K fractured from Nb/Si3N4 side. When re-heating the joints from RT to 673 K, fracture initiation gradually shifted from Si3N4 towards interfacial-compounds/Si3N4 interface and bending strengths maintained ∼220 MPa as weakening of SILVER-ABA filler was compensated by residual-stress relaxation in Si3N4. When tested at 873 K, joints fractured mainly across the Ag-rich solid solution in a ductile manner and bending strength degraded by ∼20% to 171 MPa as weakening of SILVER-ABA filler dominated.