Metallurgical Abstracts on Light Metals and Alloys vol.54
Effect of TiB orientation on four-point bending fatigue properties of TiB-reinforced Ti-3Al-2.5V alloy treated with heat extrusion
Hideyuki Hirai*, Hiroki Kurita**, Sophie Gourdet***, Keisuke Fujita*, Kenta Nakazawa**** and Shoichi Kikuchi****
*Graduate School of Integrated Science and Technology, Shizuoka University
**Department of Materials Processing, Graduate School of Engineering, Tohoku University
***Ariane Group
****Department of Mechanical Engineering, Faculty of Engineering, Shizuoka University
[Published in 29 August 2020, Vol. 238 (2020), pp. 107284]
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engfracmech.2020.107284
E-mail: kikuchi.shoichi@shizuoka.ac.jp
Key Words:Fatigue, Titanium alloy, Titanium boride, Metal composite, Fracture mechanics
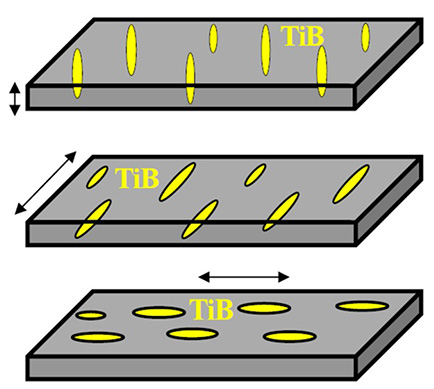
TiB-reinforced Ti-3Al-2.5V alloy, in which TiB whiskers are oriented parallel to the direction of heat extrusion, was manufactured. In order to study the effects of TiB orientation on fatigue properties in TiB-reinforced Ti-3Al-2.5V alloy, four-point bending fatigue tests were performed for plate-type samples having three different orientations of TiB whiskers at stress ratio of 0.1 under ambient conditions. The fatigue limit and fatigue life of the Ti-3Al-2.5V alloy with TiB whiskers, which are oriented parallel to the loading direction, were higher than those obtained in the case where TiB whiskers are vertical. This resulted from the reduction of the fatigue crack initiation resistance by the TiB whiskers orientation which is oriented vertical to the loading direction and the increment of the fatigue crack propagation resistance in Ti-3Al-2.5V alloy having TiB whiskers orientation which is set to be parallel to the loading direction. Hence, the fatigue properties in Ti-3Al-2.5V alloy with TiB whiskers depended on the TiB orientation.