Metallurgical Abstracts on Light Metals and Alloys vol.55
Nondestructive Nanostructure Analysis of Al/AlZn Interdiffusion Layer by Quantitative SAXS Tomography
Shan Lin*, Hiroshi Okuda*, Yukihiro Nishikawa**, Shin-ichi Sakurai**, Taizo Kabe*** and Hiroyasu Masunaga***
*Department of Materials Science and Engineering, Kyoto University
**Kyoto Institute of Technology.
***JASRI Spring-8.
[Published in Materials Transactions, vol. 62 (2021) pp. 1673–1676]
https://doi.org/10.2320/matertrans.MT-L2021012
E-mail: okuda.hiroshi.5a[at]kyoto-u.ac.jp
Key Words: SAXS tomopgraphy, interdiffusion layer, small-angle X-ray scattering, nondestructive nanostructure analysis,
Tomographic images with absolute units have been reconstructed successfully from Small Angle X-ray Scattering (SAXS) intensities of an interdiffusion layer of a precipitation strengthened model alloy cut from a multilayered Al/AlZn/Al sample after heat treatment. Cross sectional images of specimen with Zn concentration distribution was obtained from the absolute X-ray mass attenuation coefficient; the volume fraction of precipitates from the absolute SAXS integrated intensity in each voxel. Mechanical property of the same cross-section was estimated from the nanostructure and composition obtained for each voxel determined by the reconstructed images. The absolute integrated intensity and the consequent volume fraction of precipitates were reconstructed for the first time. A 2D distribution of ultimate tensile strength of the same cross-section and its yield stress with precipitates was estimated by using the absolute tomography of nanostructure for the first time.
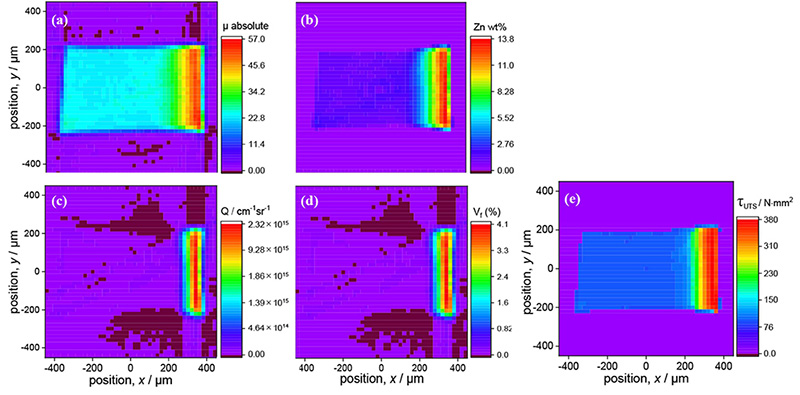
Reconstructed tomography of (a) absorption coefficient (b) Zn concentration from absorption coefficient (c) absolute integrated intensity (d) volume fraction of GP zones (e) calculated UTS distribution.
