Metallurgical Abstracts on Light Metals and Alloys vol.55
Interfacial microstructure evolution and mechanical properties of explosively welded Mg/Al alloy plates
Mami Mihara-Narita*, Konosuke Asai* Hisashi Sato*, Yoshimi Watanabe*, Hisashi Mori**, Naobumi Saito*** and Yasumasa Chino***
*Department of Physical Science and Engineering, Nagoya Institute of Technology
**UACJ Corporation, Research & Development Division
***National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology (AIST)
[Published in Journal of Materials Engineering and Performance, (2022)]
https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-022-06843-z
E-mail: narita.mami[at]nitech.ac.jp
Key Words: explosive welding, dissimilar metal joining, interlayer, residual stress, magnesium, aluminum
In this study, properties of cladding plates produced by explosive welding between magnesium alloys having different aluminum concentrations and A6005C aluminum alloy were investigated. In all cladding plates, the bonding interface has a wavy shape. Adiabatic shear bands are formed at the interface on the magnesium alloy side and deformed twins appeared at the interface due to the impact of explosive welding. Microstructure observation using scanning transmission electron microscope revealed that a thin interlayer was formed at the interface in all cladding plates. The thickness of the interlayer increased with an increase of aluminum concentration in the magnesium alloy, while the thickness was 1 μm or less. In the cross-section of the cladding plate, aluminum alloy showed a relatively higher Vickers hardness value compared with the magnesium alloy, and the hardness value increased when approaching the interface. However, no increase in hardness was determined at the interface using nanoindentation tests. Measurements of the residual stress using synchrotron radiation X-rays at the interface of cladding plates revealed that there was a tendency for tensile residual stress to occur on the Mg alloy side and compressive residual stress on the Al alloy side. This might be due to a difference in the coefficient of thermal expansion between the magnesium and aluminum alloys.
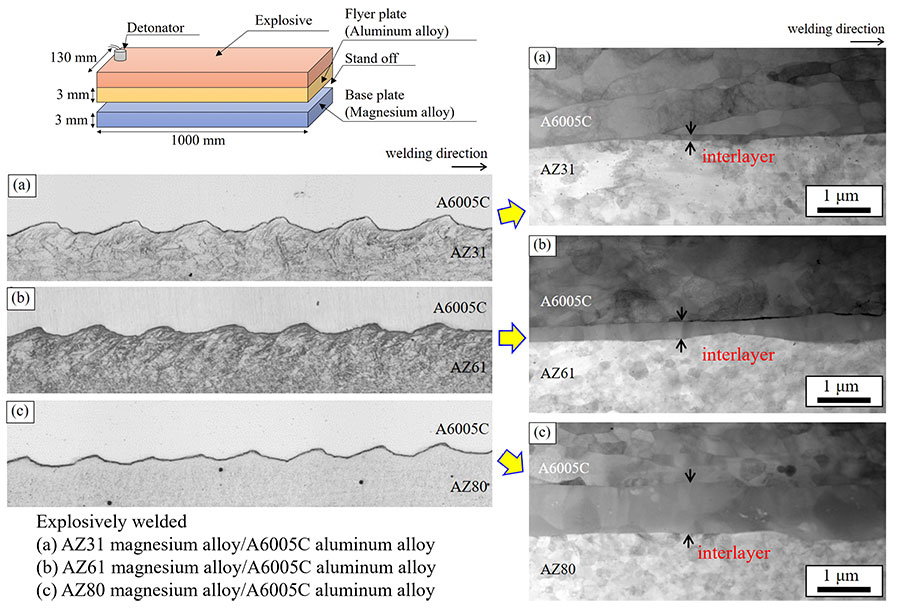
Interfacial microstructure of explosively welded magnesium/aluminum alloy cladding plates.
