Metallurgical Abstracts on Light Metals and Alloys vol.55
Analysis of the Oxidation and Nitridation of Ti-17 (Ti-5Al-2Sn-2Zr-4Mo-4Cr) Alloys with Added Si under Atmospheric Heating
Takayuki Narushima1,2), Satoshi Suzuki1), Kyosuke Ueda1), Somesh Kr. Bhattacharya2) and Ryoji Sahara2)
1)Department of Materials Processing, Tohoku University
2)Research Center for Structural Materials, National Institute for Materials Scinence
[Published in ISIJ International, Vol. 62 (2022), pp. 1512–1521]
https://doi.org/10.2355/isijinternational.ISIJINT-2022-053
E-mail: narut[at]material.tohoku.ac.jp
Key Words: oxidation, nitridation, α-case, titanium nitride, parabolic rate constant, machine learning
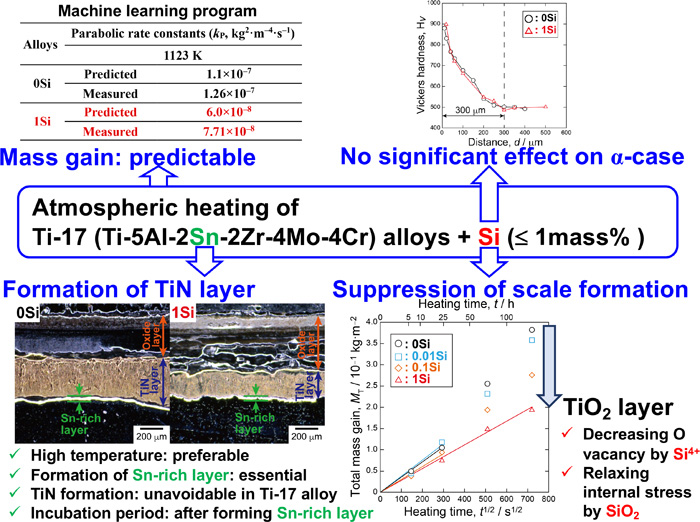
We investigated the oxidation and nitridation of a near β-type Ti-17 (Ti-5Al-2Sn-2Zr-4Mo-4Cr) alloy with up to 1 mass% of added Si. The alloys were heated in air at 923–1223 K for up to 518.4 ks. The mass gain was determined, and the scales and oxygen-rich α-case layer that were formed were analyzed. At temperatures below 1123 K, the primary product was rutile-type TiO2, along with traces of Al2O3. The presence of Si4+ decreased the oxygen vacancy concentration in TiO2, whereas the presence of SiO2 caused the relaxation of the internal stress in the scale. These factors were instrumental in lowering the parabolic rate constant and expanding the region conforming to the parabolic rate law. A TiN layer was detected beneath the oxide layer at 1223 K. At the interface between the TiN layer and the Ti alloy, a Sn-rich layer was observed. Both the presence of the Sn-rich layer and the incubation period following the formation of the Sn-rich layer play a crucial role in the formation of the TiN layer. Meanwhile, Si addition had no discernible effect on the formation of the α-case. The parabolic rate constants that were predicted via machine learning concurred well with the measured values. The current study is the first report that describes the scale and α-case formation in Ti-17 alloys, and it may serve as a guideline for determining the optimal application conditions, designing a practical manufacturing process, and improving the oxidation resistance of Ti-17 alloys with Si.