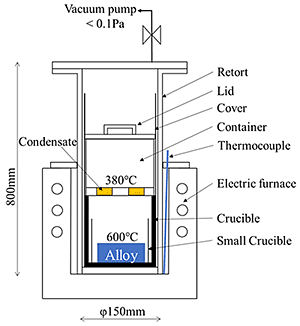
High purity magnesium sheet was prepared by vacuum distillation and plastic working. Figure 1 shows schematic diagram of vacuum distillation apparatus.
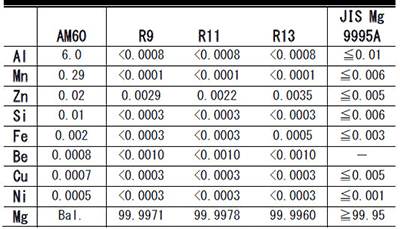
Figure 2 shows outward appearance of vacuum distilled and extruded (R13) specimen. Figure 3 shows outward appearance of vacuum distilled, extruded (R13) and rolled specimen. The Plastic working was extrusion and rolling. The high purity magnesium sheet can be made from vacuum distillation and plastic working. Table 1 shows chemical compositions of vacuum distilled and extruded specimens.
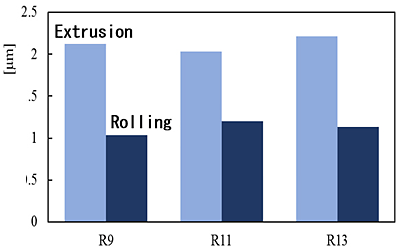
Figure 4 shows arithmetic average roughness (Ra) of vacuum distilled and extruded specimens and vacuum distilled, extruded and rolled specimens. After vacuum distillation and extrusion, the surface roughness of the specimen was improved by rolling.
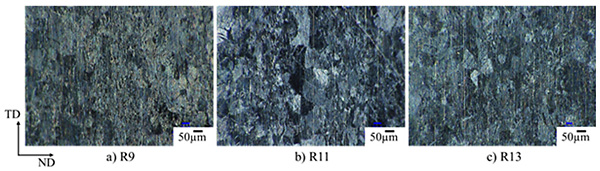
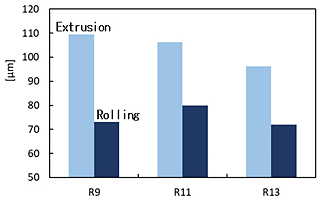
Figure 5 shows microstructures of vacuum distilled and extruded specimens. Figure 6 shows microstructures of vacuum distilled, extruded and rolled specimens. Crystal grain of the vacuum distilled, extruded and rolled specimen was smaller than that of the vacuum distilled and extruded specimen. Figure 7 shows grain size of vacuum distilled and extruded materials and vacuum distilled, extruded and rolled specimens.
Figure 8 shows hardness of vacuum distilled and extruded materials and vacuum distilled, extruded and rolled specimens. Hardness of the vacuum distilled, extruded and rolled specimen was larger than that of the vacuum distilled. Extruded specimen. 90°direction of ultimate tensile strength becomes larger than 0°direction to rolling direction for the vacuum distilled, extruded and rolled specimen.